Guidelines for PFAS Waste Management at Treatment Facilities
Guidelines for PFAS Waste Management at Treatment Facilities
Blog Article
Your Guide to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Benefits
The occurrence of PFAS contamination in water sources demands a complete understanding of readily available treatment technologies. Each technology not only targets certain PFAS substances but also plays an important duty in enhancing general water quality and securing environmental honesty.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
Recognizing PFAS contamination is critical for resolving its prevalent effect on environmental and human wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) are a team of synthetic chemicals widely made use of in different commercial and consumer products as a result of their water- and grease-resistant properties. Typically located in firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, and water-repellent materials, PFAS have gone into the atmosphere via production procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from landfills
When released, these substances continue in the environment, bring about prevalent contamination of dirt and water resources. Their distinct chemical framework, defined by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, renders them immune to destruction, leading to a sensation referred to as "permanently chemicals." As a result, PFAS can accumulate in the human body and the food web, potentially triggering adverse health and wellness results, including body immune system disruption, developing issues, and an increased threat of specific cancers cells.
Regulatory agencies and health companies are significantly acknowledging the importance of PFAS contamination, motivating initiatives to check, evaluate, and minimize its effects. Recognizing the paths of PFAS contamination is important for educating public plan and establishing efficient strategies to protect both environmental and human health.
Review of Therapy Technologies
Different therapy modern technologies have been established to resolve the difficulties postured by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These modern technologies can be generally categorized into numerous groups, each with its unique devices and efficiency in eliminating PFAS compounds.
One prominent technique is ion exchange, which utilizes material products to capture and remove PFAS from contaminated water. This method is specifically effective for short-chain PFAS and can attain substantial decreases in focus levels. One more modern technology, advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs), uses solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down PFAS into much less unsafe substances. AOPs appropriate for treating a variety of PFAS compounds yet may call for cautious optimization to make the most of effectiveness.

Activated Carbon Filtration
Triggered carbon filtration is an extensively made use of technique for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water, understood for its capacity to adsorb a broad range of organic compounds. This technology utilizes activated carbon, a highly porous material with a comprehensive surface location, which facilitates the binding of PFAS particles with physical adsorption. The efficiency of turned on carbon in getting rid of PFAS is affected by a number of aspects, consisting of the sort of carbon used, the call time, and the concentration of PFAS in the water.
Among the advantages of turned on carbon filtration is its convenience; it can be carried out in numerous arrangements, such as granular turned site web on carbon (GAC) systems or powdered activated carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) systems. GAC systems are usually employed in larger-scale applications, while PAC can be utilized in smaller or temporary arrangements. Furthermore, the innovation is relatively very blog here easy to operate and preserve, making it accessible for several water treatment facilities.

Ion Exchange Solution
Ion exchange systems represent an additional effective strategy for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water, complementing techniques like turned on carbon filtration. These systems operate the principle of exchanging ions in the water with ions hung on a resin material. Ion exchange materials can be specifically created to target the adversely billed PFAS compounds, efficiently recording them and permitting cleaner water to travel through.
Among the main benefits of ion exchange systems is their ability to eliminate a vast array of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variations. This flexibility makes them appropriate for numerous applications, varying from metropolitan water therapy to commercial processes. In addition, ion exchange systems can usually accomplish reduced discovery restrictions for PFAS compared to a few other treatment methods, thus boosting water top quality.
Nonetheless, it is vital to keep an eye on and handle the regrowth of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decrease gradually due to saturation. Proper upkeep and substitute of the material are vital for sustaining the system's efficiency. Overall, ion exchange systems offer a trustworthy and reliable solution for PFAS elimination, adding dramatically to secure drinking water criteria and environmental management.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) use effective oxidants to properly deteriorate PFAS compounds in polluted water. These her explanation ingenious treatment techniques create highly reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can break down intricate PFAS particles into less hazardous byproducts. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs commonly utilize combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, improving the oxidation potential and improving deterioration effectiveness
The primary advantage of AOPs exists in their ability to target a broad variety of PFAS compounds, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variations. This flexibility is essential, as PFAS contamination commonly involves mixtures of various compounds with varying chemical structures. Additionally, AOPs can be integrated right into existing water treatment systems, making them a useful service for many municipalities and sectors.
Nevertheless, the execution of AOPs can be resource-intensive, calling for cautious factor to consider of functional expenses and energy usage. In addition, while AOPs work in damaging down PFAS, they may not entirely eliminate all results, demanding further treatment steps - m270 pfas treatment. Generally, AOPs represent a promising method for resolving PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water resources and boosted public health protection
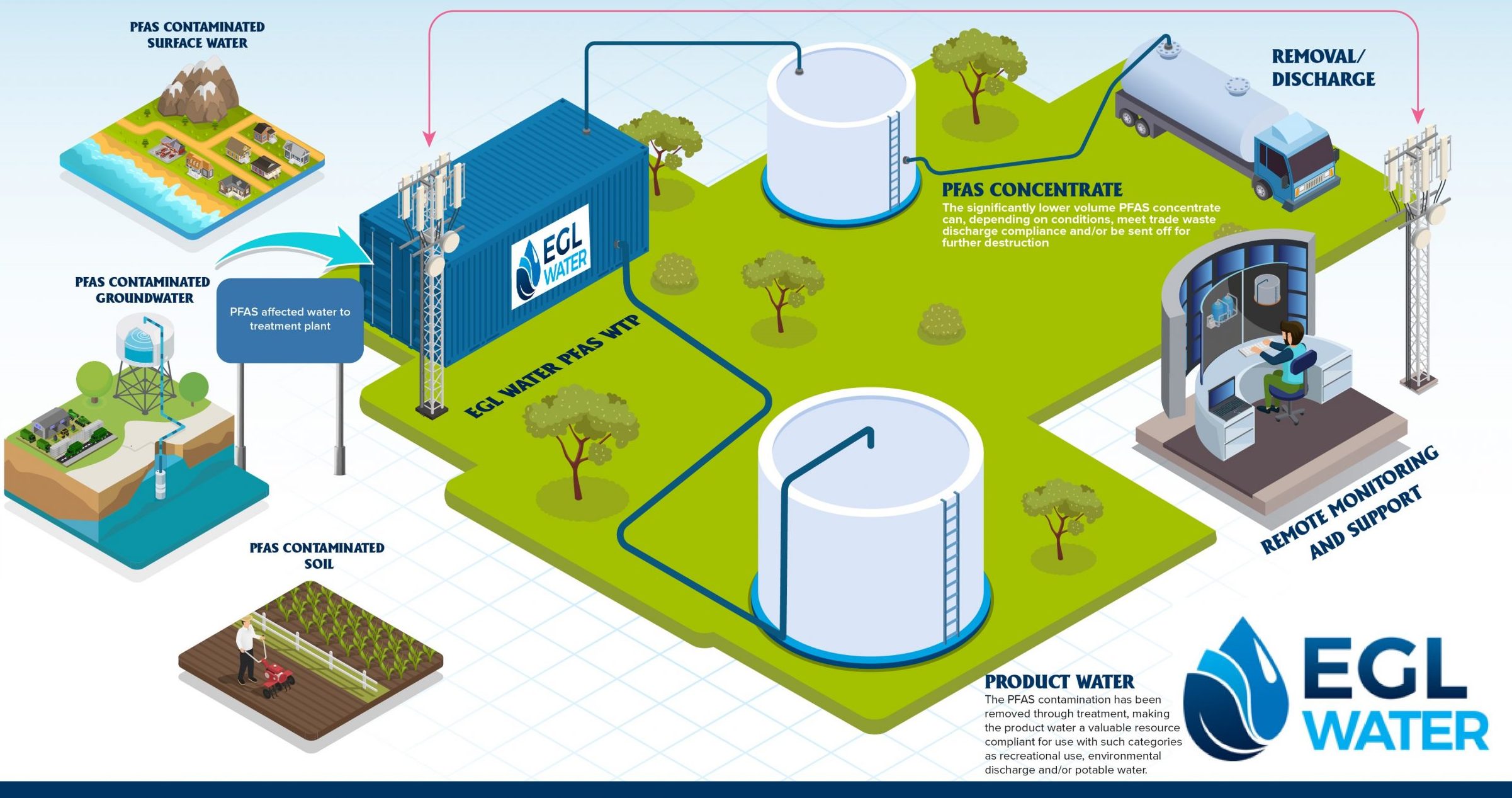
Conclusion
In final thought, attending to PFAS contamination calls for a thorough understanding of offered therapy technologies. Turned on carbon filtering, ion exchange systems, and progressed oxidation processes each existing special benefits for properly removing these unsafe substances from water resources. By selecting the suitable innovation, areas can improve water top quality, safeguard public wellness, and alleviate the environmental threats connected with PFAS direct exposure. Proceeded research study and execution of these techniques are essential for effective management of PFAS contamination in impacted areas.
Report this page